It can be an understatement to say that the Earth’s magnetic subject is necessary. It’s one of many causes we’re in a position to stay on this rock tumbling by way of area, and it additionally provides us the attractive aurora borealis. So it is a reasonably large deal when it adjustments — and such a change is going on proper now within the South Atlantic Ocean, the place the magnetic subject’s weakest level seems to be rising.
The European Space Agency spent 11 years finding out the magnetic subject through the company’s Swarm operation. Part of the mission was to measure and observe the South Atlantic Anomaly, a pronounced weak spot within the Earth’s magnetic subject that sits over South America. This was initially found in 1958 when satellites first began measuring radiation across the Earth, so its existence is nothing new.
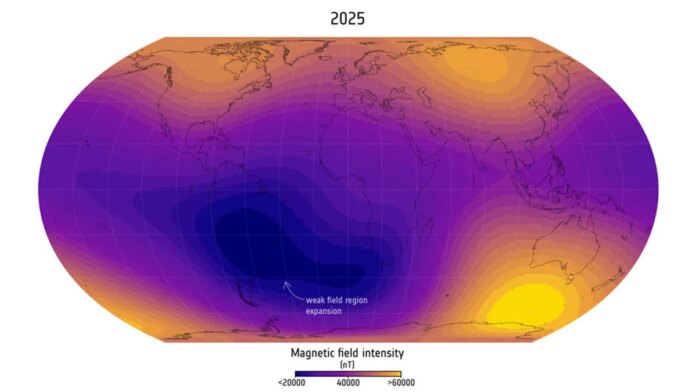
However, knowledge from the Swarm mission reveals that the weak spot has been quickly rising, extending its presence throughout the Atlantic Ocean towards Africa.
Why is the weak spot rising?
Per the ESA, this phenomenon could be greatest defined by unusual behaviors far inside the Earth on the boundary the place the Earth’s liquid outer core meets the rocky mantle layer. This boundary, known as reverse flux patches, is performing humorous and inflicting the magnetic subject to weaken in that one spot.
“Normally, we would count on to see magnetic subject traces popping out of the core within the southern hemisphere,” says C.C. Finlay, lead creator of the research and professor of geomagnetism on the Technical University of Denmark. “But beneath the South Atlantic Anomaly, we see surprising areas the place the magnetic subject, as a substitute of popping out of the core, goes again into the core. Thanks to the Swarm knowledge, we are able to see one in all these areas shifting westward over Africa, which contributes to the weakening of the South Atlantic Anomaly on this area.”
In addition to the South Atlantic Anomaly, the Swarm mission additionally confirmed {that a} stronger part of the magnetic subject over Canada was additionally getting weaker, whereas the one over Siberia was getting stronger.
A hazard to satellites in all places
The weakened zone will not have a major impression on people, because the ambiance primarily offers with the weather that have an effect on the Earth’s floor. As NASA says, the weakening continues to be inside what scientists contemplate “regular variation,” so day by day life is not affected.
However, issues in low Earth orbit aren’t so fortunate. Per the ESA, satellites and different spacecraft passing by way of the area will face increased radiation publicity that “can result in malfunctions or harm to essential {hardware}, and even blackouts.”
As Finlay notes within the research, area businesses take the SAA into consideration when constructing fashionable spacecraft, satellites and different space-worthy know-how, so not solely are present satellites prone to harm, however the increasing weak spot may even have an effect on how future satellites and spacecraft are designed.
The ESA says that the Swarm mission will proceed to assemble knowledge in regards to the Earth’s magnetic subject into the foreseeable future.
“It’s actually great to see the large image of our dynamic Earth due to Swarm’s prolonged timeseries,” says ESA Swarm Mission Manager Anja Stromme. “The satellites are all wholesome and offering glorious knowledge, so we are able to hopefully prolong that report past 2030, when the photo voltaic minimal will permit extra unprecedented insights into our planet.”